The Impact of Contraceptives on Women’s Health and Empowerment
Contraceptives are a cornerstone of women’s health and empowerment, offering benefits that reach far beyond pregnancy prevention. This blog seeks to dispel common myths surrounding contraceptives and underscore their profound impact on women’s overall well-being and empowerment.
Debunking Common Myths and Misconceptions About Contraceptives
Myth: Contraceptives cause weight gain
Fact: While slight weight changes may occur, contraceptives do not directly lead to significant weight gain. Factors like metabolism and lifestyle have a more substantial impact on weight.
Myth: Contraceptives decrease fertility
Fact: Contrary to belief, contraceptives do not permanently affect fertility. Once discontinued, a woman’s fertility typically returns to normal, easing concerns about fertility issues.
Myth: Contraceptives are solely for preventing pregnancy
Fact: In addition to preventing unplanned pregnancies, contraceptives offer various health benefits, like menstrual cycle regulation, reduced cramps, and improved skin conditions.
Myth: Contraceptives protect against STIs
Fact: Not all contraceptives safeguard against sexually transmitted infections. While effective in preventing pregnancy, contraceptives like pills do not provide STI protection, emphasizing the need for combined methods.
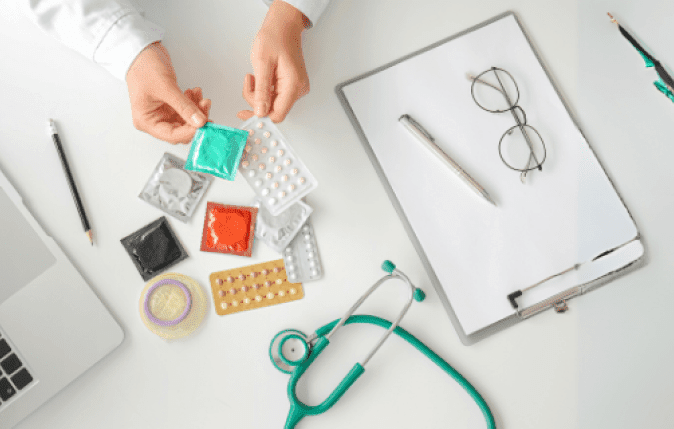
Understanding Different Types of Contraceptives: Which is Better?
When selecting a contraceptive method, understanding the available options is crucial. Here’s a glimpse of common contraceptive types:
Hormonal Contraceptives:
- Birth Control Pills, Patches, Rings, Injections: These methods suppress ovulation and alter cervical mucus to prevent sperm from fertilizing the egg.
Barrier Contraceptives:
- Condoms, Diaphragms: They physically obstruct sperm from reaching the egg.
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs):
- Hormonal and Non-Hormonal IUDs: Small devices placed in the uterus offering long-term contraceptive protection.
Sterilization:
- Tubal ligation, Vasectomy: Permanent procedures for individuals seeking sterilization.
Natural Family Planning:
- Tracking Fertile Days: Involves monitoring cycles to avoid intercourse during fertile periods.
Factors Affecting the Selection of Contraceptive Pills as a Method
Several factors guide the choice of contraceptive pills for birth control:
- Effectiveness: Opting for highly effective pills when taken correctly.
- Medical History: Considering existing health conditions.
- Side Effects: Discussing potential effects like mood changes and weight fluctuations.
- Hormonal Composition: Deciding between combination or progestin-only pills.
- Convenience and Compliance: Adhering to dosing schedules and daily routines.
- Non-Contraceptive Benefits: Assessing additional benefits beyond birth control.
- Family Planning Goals: Aligning contraceptive choice with family planning objectives.
- Cost and Accessibility: Considering affordability and availability.
- Age and Lifestyle Factors: Tailoring choices based on age, lifestyle, and preferences.
- Consultation with Healthcare Provider: Seeking expert advice for personalized recommendations.
Can fertility be affected by contraceptives?
Fertility is a topic of concern for many individuals considering contraceptive use. Here’s some detailed information related to how contraceptives can affect fertility:
-
Temporary Suppression: Some contraceptives, especially hormonal methods like birth control pills, patches, injections, and hormonal IUDs, work by temporarily suppressing ovulation. While fertility is temporarily inhibited during contraceptive use, discontinuing these methods usually allows fertility to return to its normal state.
-
Non-Hormonal Methods: Non-hormonal contraceptives like barrier methods (condoms, diaphragms) and copper IUDs do not impact fertility in the long term. Once these methods are discontinued, fertility typically returns promptly.
-
Individual Responses: Every individual’s body responds differently to contraceptives. While most experience a return to fertility after stopping contraceptive use, some may have variations in the time taken for fertility to resume.
-
Long-Term Contraceptive Use: Prolonged use of certain contraceptive methods, such as long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) like hormonal IUDs or implants, may delay the return to fertility compared to short-term methods like birth control pills.
-
Consultation with Healthcare Provider: If concerns about fertility arise, consulting a healthcare provider or gynecologist is essential. They can provide personalized guidance based on individual health history, contraceptive method used, and specific fertility goals.
In conclusion, while contraceptives can temporarily affect fertility by suppressing ovulation, most methods do not have a lasting impact. Understanding how contraceptives influence fertility helps individuals make informed decisions aligned with their family planning goals. This comprehensive understanding of contraceptives enhances women’s health decisions, promotes autonomy, and supports their overall well-being and empowerment.
-