Recognizing GI Bleeding Symptoms: A Comprehensive Guide
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding can range from mild to severe and may indicate underlying health issues that require prompt medical attention. Recognizing the symptoms of GI bleeding is crucial for early detection and intervention. In this blog, we’ll explore the various signs and symptoms of GI bleeding, helping you understand what to look out for and when to seek medical help.
Understanding GI Bleeding
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding can indicate underlying health issues that require prompt medical attention. Recognizing its symptoms is crucial for early detection and intervention. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the various signs and symptoms of GI bleeding to help you understand what to look out for and when to seek medical help.
Recognizing Symptoms of GI Bleeding
GI bleeding can manifest in various ways and is classified as either visible bleeding, such as bloody stools or vomit, or occult bleeding, which is not visible to the naked eye. Common symptoms include:
- Blood in Stools: Presence of bright red blood or dark, tarry stools.
- Vomiting Blood: Description of vomit as coffee-ground or bright red blood.
- Rectal Bleeding: Blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl after a bowel movement.
- Abdominal Pain or Discomfort: Experience of abdominal pain, cramping, or discomfort.
- Weakness and Fatigue: Symptoms of chronic or recurrent GI bleeding leading to iron deficiency anemia.
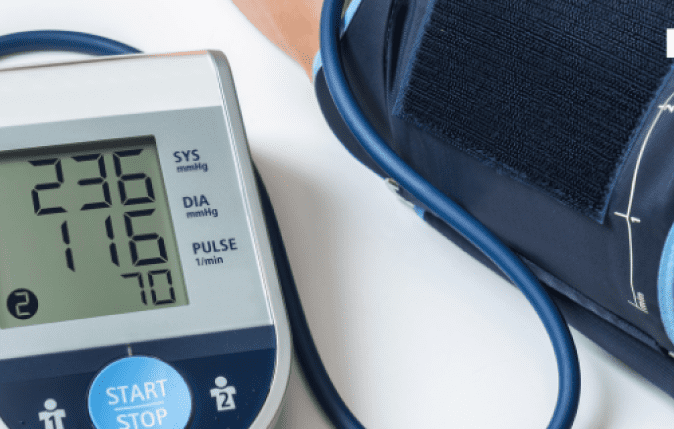
- Fainting or Lightheadedness: Symptoms associated with severe GI bleeding, such as lightheadedness, dizziness, fainting, or shock.
Understanding the Causes of GI Bleeding
The causes of GI bleeding can be diverse and may include various conditions affecting different parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Common causes are:
- Peptic ulcers
- Gastritis or erosive gastritis
- Esophageal varices
- Mallory-Weiss tears
- Colorectal polyps or cancer
- Diverticulosis
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Identifying Risk Factors for GI Bleeding
Several factors may increase the risk of GI bleeding, including advanced age, history of peptic ulcer disease, chronic use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), alcohol abuse, smoking, and certain medical conditions like Helicobacter pylori infection, Crohn’s disease, or ulcerative colitis.
When to seek Help:
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly:
- Persistent or Severe Abdominal Pain: Especially if accompanied by vomiting blood or passing black, tarry stools.
- Significant Rectal Bleeding: Particularly if it persists or is associated with other symptoms like weakness or dizziness.
- Symptoms of Anemia: Such as weakness, fatigue, or shortness of breath, especially if you have a history of GI bleeding.
- Changes in Mental Status: Such as confusion, disorientation, or loss of consciousness, which could indicate severe bleeding and require emergency care.
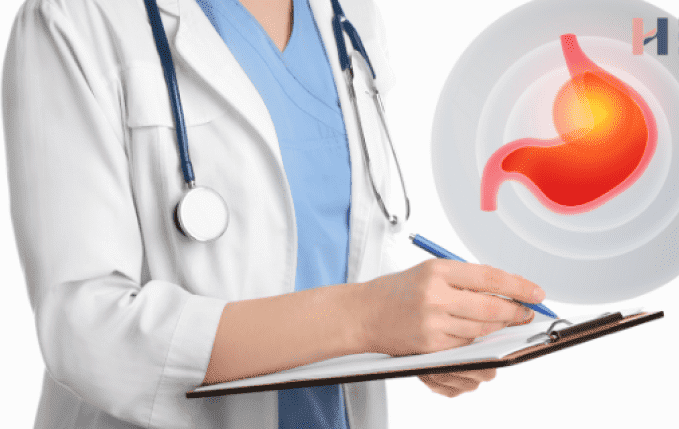
Recognizing the symptoms of GI bleeding is essential for early detection and appropriate management. If you experience any signs of GI bleeding, such as blood in stools, rectal bleeding, or abdominal pain, it’s crucial to seek medical evaluation promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can help identify the underlying cause of GI bleeding and prevent potential complications, ensuring optimal health and well-being.