Unlocking the Connection Between Diabetes and Neuropathy: A Comprehensive Guide
In the intricate interplay of health conditions, diabetes and neuropathy are closely intertwined. Diabetes, a widespread metabolic disorder, often sets the stage for neuropathy, a condition characterized by nerve damage and ensuing symptoms. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, identifying early warning signs, and adopting preventive measures are crucial components in effectively managing these conditions. Join us as we delve into the complexities of diabetes-induced neuropathy and elucidate why early intervention is paramount.
Unraveling How Diabetes Leads to Neuropathy: Mechanisms and Risk Factors
Diabetes triggers a series of physiological changes that can adversely affect nerves throughout the body. The primary mechanism linking diabetes to neuropathy involves prolonged exposure to elevated glucose levels, resulting in nerve fiber damage over time. Additionally, fluctuations in insulin levels, inflammation, and oxidative stress contribute to nerve damage. Certain risk factors exacerbate this process, including poorly controlled blood sugar, obesity, smoking, and genetic predispositions. Understanding these mechanisms empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their diabetes and mitigating neuropathy risk.
The Critical Importance of Early Intervention: Recognizing Early Warning Signs
The proverb “prevention is better than cure” holds particularly true in the context of diabetic neuropathy. Early intervention can halt or slow the progression of nerve damage, preserving quality of life and preventing debilitating complications. Recognizing the subtle warning signs is crucial: tingling or numbness in the extremities, burning sensations, muscle weakness, and sensitivity to touch. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and annual foot exams are indispensable for detecting neuropathy in its early stages, facilitating timely intervention and better outcomes.
Nurturing Wellness Through Diet, Exercise, and Stress Reduction: Foundations of Neuropathy Prevention
A holistic lifestyle forms the cornerstone of preventing diabetic neuropathy. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps regulate blood sugar levels and mitigate nerve damage. Incorporating regular exercise into daily routines enhances circulation, promotes nerve function, and fosters overall well-being. Stress reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga alleviate inflammation and oxidative stress, reducing neuropathy risk factors. Small lifestyle adjustments yield significant benefits in safeguarding against the onset and progression of diabetic neuropathy.
Strategies for Preventing Neuropathy in Diabetes Patients
Empowered with knowledge and determination, individuals with diabetes can proactively reduce their risk of developing neuropathy. Implementing practical tips can make a tangible difference:
- Maintain optimal blood sugar control through dietary modifications, medication adherence, and regular monitoring.
- Manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels to safeguard vascular health.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption to mitigate nerve damage.
- Prioritize foot care by conducting regular inspections for cuts, blisters, and sores, and wearing supportive footwear.
- Attend regular check-ups with healthcare providers to assess nerve function and address any concerns promptly.
Recognizing Signs, Symptoms, and Diagnosing Diabetic Neuropathy
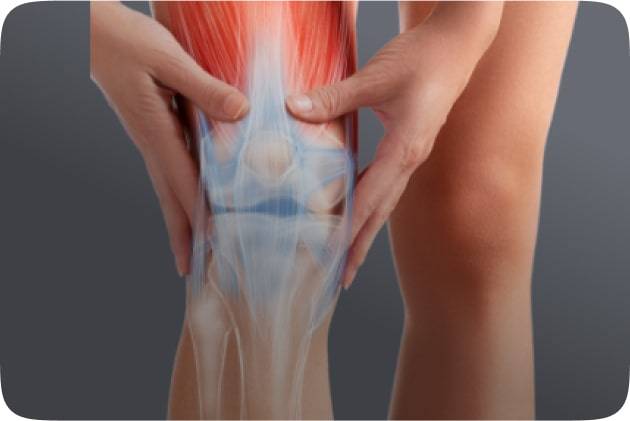
Diabetic neuropathy presents with diverse symptoms, each posing unique challenges to individuals’ well-being. Peripheral neuropathy, affecting the extremities, often manifests as tingling, numbness, or pain in the feet and hands. Autonomic neuropathy disrupts involuntary bodily functions, leading to digestive issues, urinary problems, and cardiovascular irregularities. Proximal neuropathy causes muscle weakness and pain in the thighs, hips, or buttocks. Timely diagnosis is imperative, typically involving a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, nerve function tests, and imaging studies. Early detection facilitates prompt intervention and optimal management strategies.
In the intricate dance between diabetes and neuropathy, awareness and action are pivotal for effective management. By understanding the underlying mechanisms, recognizing warning signs, embracing a healthy lifestyle, and implementing preventive measures, individuals can navigate this challenging terrain with resilience and optimism. Let us forge a path towards wellness, empowered by knowledge and fueled by a shared commitment to thriving despite the odds.