Understanding Abdominal Pain after Eating: Is it Linked to Gastroparesis?
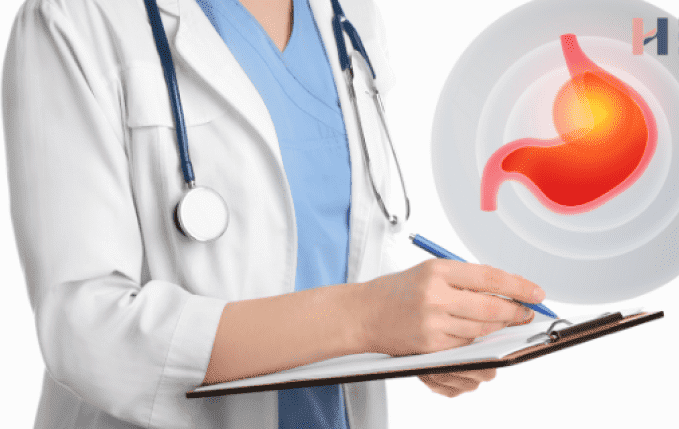
Are you experiencing abdominal pain following meals? This discomfort might be signaling an underlying condition such as gastroparesis, a condition that affects the normal spontaneous movement of the muscles in your stomach. Let’s delve into what gastroparesis is, its potential symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and management strategies.
What is Gastroparesis?
Gastroparesis, also known as delayed gastric emptying, is a condition characterized by the partial paralysis of the stomach, leading to delayed digestion and emptying of food from the stomach into the small intestine. This can result in various symptoms, including abdominal pain after eating, bloating, nausea, and a feeling of fullness after consuming only a small amount of food.
Symptoms of Gastroparesis
In addition to abdominal pain after eating, individuals with gastroparesis may experience symptoms such as:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Feeling full quickly when eating
- Bloating
- Heartburn
- Fluctuations in blood sugar levels
Causes of Gastroparesis
Gastroparesis can be caused by various factors, including:
- Diabetes
- Post-surgical complications
- Neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis
- Medications that affect the gastrointestinal system
- Connective tissue disorders
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
If you are experiencing persistent abdominal pain after eating, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. Diagnostic measures for gastroparesis may include gastric emptying studies, upper endoscopy, and imaging tests. Treatment options may involve dietary modifications, medication to stimulate stomach emptying, and in severe cases, surgical interventions.
Lifestyle Changes and Management
Managing gastroparesis involves making certain lifestyle adjustments, including:
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals
- Consuming foods low in fiber and fat
- Chewing food thoroughly
- Staying hydrated
- Avoiding lying down right after eating
In conclusion, abdominal pain following meals can be indicative of various medical conditions, including gastroparesis. If you are experiencing persistent symptoms, seeking medical attention is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Take proactive steps to understand and address your symptoms, and remember that early intervention can significantly improve your quality of life.