Unraveling the Mystery of Muscle Pain vs. Arthritis!
Muscle pain and arthritis are two distinct but often misunderstood conditions that can cause discomfort and hinder daily activities. Distinguishing between the two is crucial for proper diagnosis and effective treatment. In this blog, we will explore the differences between muscle pain and arthritis, debunk common myths, and discuss when it’s essential to consult a physician.
Distinguishing Between Muscle Pain and Arthritis:
- Location and Nature of Pain:
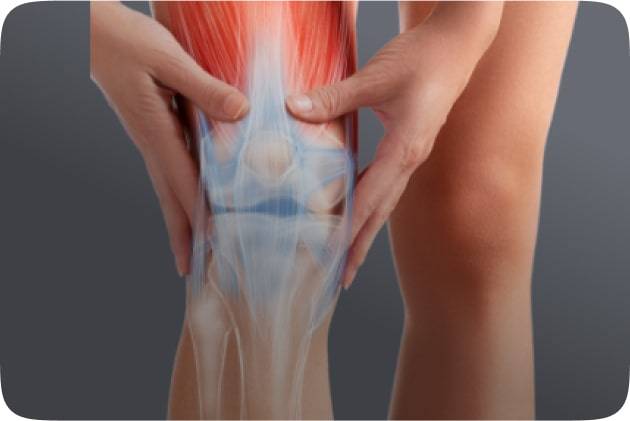
- Muscle Pain: Typically occurs in specific muscle groups and is often associated with overuse, strain, or injury. It tends to be localized and may feel sore or achy.
- Arthritis: Affects joints and can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling. Arthritis-related pain is usually concentrated in joints and may involve multiple areas of the body.
- Onset and Duration:
- Muscle Pain: Generally arises after physical activity or injury and may subside with rest or conservative measures.
- Arthritis: Often develops gradually and persists over time, becoming a chronic condition. Morning stiffness is a common characteristic of arthritis-related pain.
- Inflammatory Markers:
- Muscle Pain: Typically lacks systemic signs of inflammation like redness and swelling.
- Arthritis: Involves inflammation of the joints, leading to visible swelling, warmth, and sometimes redness in the affected areas.
Common Misconceptions about Arthritis-Related Muscle Pain:
- All Pain is Arthritis:
- Myth: Every ache or pain in the muscles is a sign of arthritis.
- Reality: Muscle pain can result from various causes, and not all muscle pain is linked to arthritis.
- Only the Elderly Experience Arthritis:
- Myth: Arthritis only affects older individuals.
- Reality: While arthritis is more common in older adults, it can affect people of all ages, including children.
- Arthritis Only Affects Joints:
- Myth: Arthritis exclusively involves joint pain.
- Reality: Arthritis can lead to muscle pain due to the inflammation of surrounding tissues and structures.
How Arthritis-Related Muscle Pain Differs from Other Causes:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis vs. Osteoarthritis:
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that can affect multiple joints and cause muscle pain due to systemic inflammation.
- Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease where the cartilage wears down, leading to joint pain and, in turn, muscle pain.
- Fibromyalgia:
- A condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness.
- Unlike arthritis, fibromyalgia primarily targets muscles and soft tissues without causing joint damage.
When to Consult a Physician:
- Persistent Pain:
- If muscle or joint pain persists for an extended period, especially if it worsens over time.
- Difficulty Performing Daily Activities:
- When pain interferes with daily tasks, such as walking, climbing stairs, or gripping objects.
- Visible Signs of Inflammation:
- If there are visible signs of inflammation, such as swelling, redness, or warmth around joints.
Distinguishing between muscle pain and arthritis is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management. Understanding the nuances of each condition, dispelling common myths, and recognizing when to seek professional medical advice empowers individuals to take control of their health and well-being. If in doubt, consulting a healthcare professional ensures a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment plan tailored to the specific needs of the individual.