How Does Air Pollution Affect Our Lungs?
Our lungs are our body’s primary interface with the external environment, responsible for delivering oxygen to the bloodstream while removing carbon dioxide. However, when exposed to air pollution, this essential organ faces a multitude of challenges:
1. Respiratory Irritation:
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): These fine particles can infiltrate deep into the lungs, leading to inflammation and irritation of the airways. This often manifests as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
- Ground-Level Ozone: Elevated levels of ground-level ozone can inflict lasting damage on lung tissue, compromising lung function and exacerbating respiratory symptoms.
2. Increased Susceptibility to Infections:
- Weakened Immunity: Air pollutants can weaken the immune system, making individuals more vulnerable to respiratory infections like bronchitis and pneumonia.
3. Aggravation of Existing Conditions:
- Asthma: Air pollution is a well-known trigger for asthma attacks, making it difficult for individuals with asthma to manage their condition effectively.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Long-term exposure to air pollution can exacerbate COPD symptoms, leading to more frequent hospitalizations and worsening quality of life for affected individuals.
What Is the Effect of Air Pollution on Human Health?
The detrimental impacts of air pollution extend far beyond the respiratory system, affecting human health in multifaceted ways:
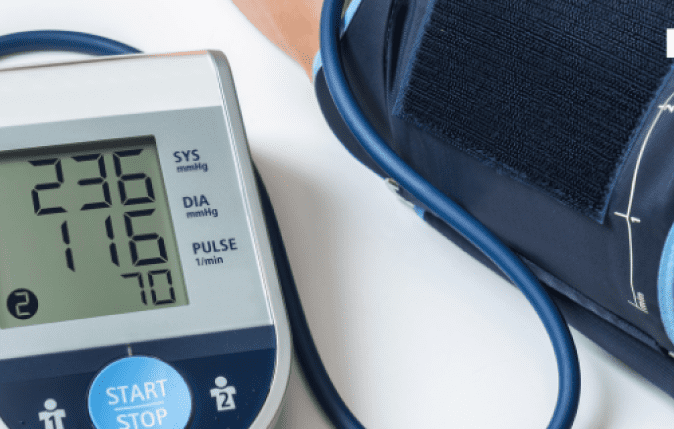
1. Cardiovascular Problems:
- Heart Disease: Prolonged exposure to air pollution elevates the risk of heart diseases, including heart attacks and strokes.
- Hypertension: Air pollution can elevate blood pressure levels, contributing to hypertension, a significant risk factor for heart disease.
2. Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes:
- Preterm Birth: Pregnant women exposed to air pollution face an increased risk of giving birth prematurely, which can lead to various health complications for the infant.
- Low Birth Weight: Air pollution is associated with low birth weight, potentially affecting the long-term health and development of the newborn.
3. Mental Health Implications:
- Stress and Anxiety: Living in areas with high air pollution levels can contribute to elevated stress and anxiety levels, impacting overall mental well-being.
How Does Air Pollution Cause Health Problems?
Understanding the intricate mechanisms by which air pollution wreaks havoc on our health is essential:
1. Inflammation:
- Airway Inflammation: Inhaling pollutants triggers inflammation in the airways, leading to conditions such as asthma and bronchitis.
2. Oxidative Stress:
- Cellular Damage: Air pollutants induce oxidative stress, causing damage to cells and DNA, increasing the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer.
3. Systemic Effects:
- Bloodstream Entry: Ultrafine particles can enter the bloodstream, disseminating pollutants throughout the body and affecting various organs.
4. Immune System Compromise:
- Weakened Immunity: Air pollution can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Conclusion
Air pollution is a complex and pervasive problem that poses a significant risk to our health, primarily affecting our respiratory system. Fine particulate matter and ground-level ozone can lead to inflammation and respiratory distress, while long-term exposure can worsen chronic conditions like asthma and COPD.
Beyond the lungs, air pollution raises the risk of cardiovascular issues, adverse pregnancy outcomes, and mental health concerns. Understanding the mechanisms of air pollution’s impact on our health is vital for informed decision-making and advocating for cleaner air.
To mitigate these effects, individuals, communities, and governments must work together to reduce air pollution through policies, sustainable practices, and lifestyle changes. By collectively taking action, we can breathe easier, safeguard our health, and ensure a healthier future for generations to come.